Health Benefits of Ginger
Ginger (Zingiber officinale) is a widely used medicinal root valued for both its culinary and therapeutic properties.
For centuries, it has been incorporated into traditional medicine systems, and modern research now confirms many of its health benefits.
Today, ginger is recognized as a functional food that supports digestion, immunity, inflammation control, and metabolic health.
 [Infographic: Key Health Benefits of Ginger]
[Infographic: Key Health Benefits of Ginger]Nutritional Profile of Ginger
Although ginger is usually consumed in small amounts, it provides valuable nutrients and powerful phytochemicals.
| Nutrient | Role in the Body |
|---|---|
| Vitamin B6 | Supports brain function and metabolism |
| Vitamin C | Boosts immune defense and antioxidant protection |
| Magnesium | Supports muscle and nerve function |
| Potassium | Helps regulate blood pressure |
| Gingerols & Shogaols | Provide anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects |
Major Health Benefits of Ginger
1. Improves Digestion and Gut Health
Ginger stimulates digestive enzymes and promotes efficient movement of food through the stomach.
- Reduces bloating and gas
- Helps relieve indigestion
- Improves stomach emptying
- Reduces nausea and vomiting
2. Reduces Inflammation and Pain
The anti-inflammatory compounds in ginger help block pathways that cause chronic inflammation.
- Relieves muscle soreness after exercise
- Reduces joint stiffness in arthritis
- Helps ease menstrual pain
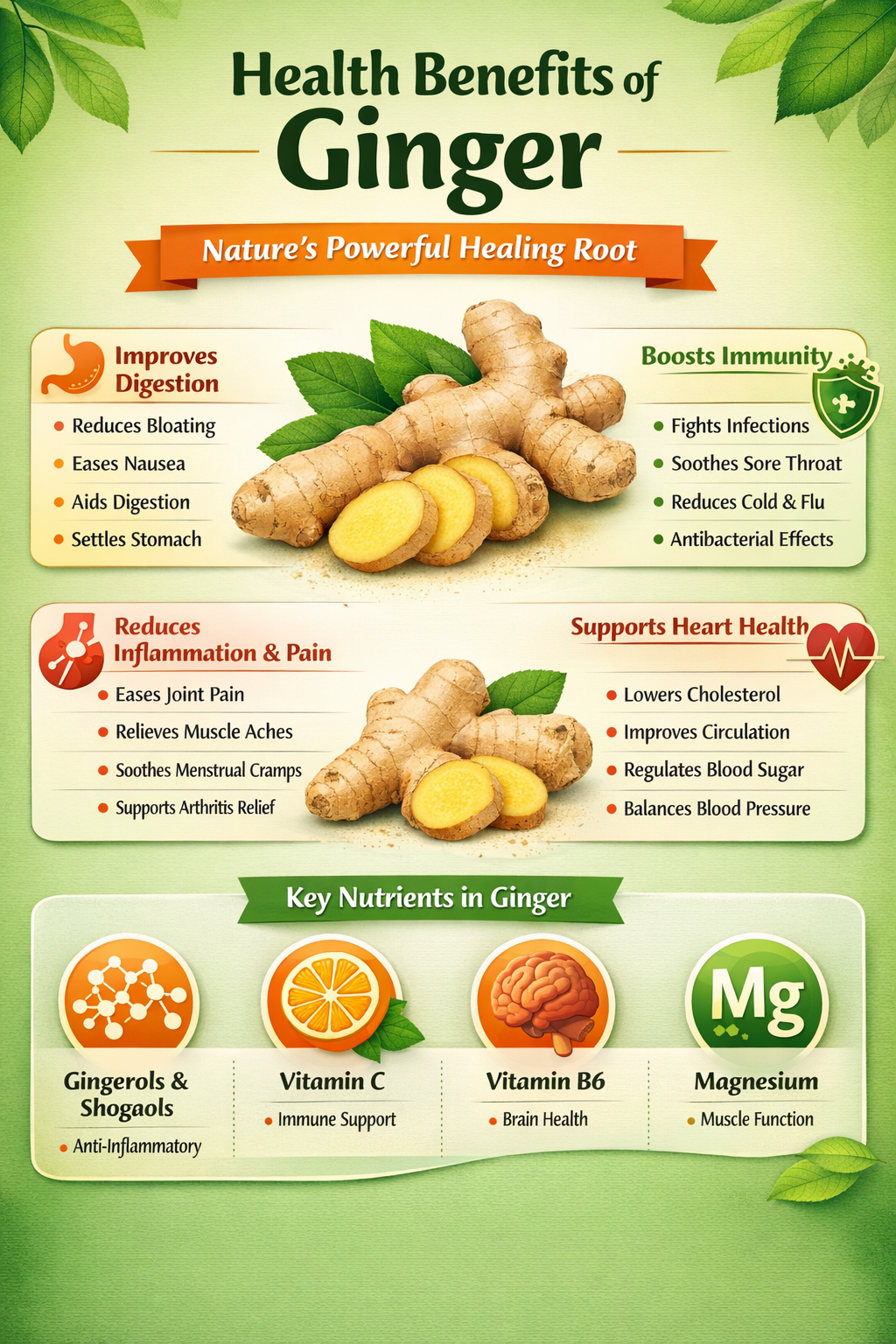
3. Supports Immune Function
Ginger has antimicrobial and antiviral properties that help the body fight infections.
- May reduce severity of colds and flu
- Soothes sore throat and cough
- Helps inhibit bacterial growth
4. Supports Heart and Metabolic Health
Research suggests ginger may support cardiovascular and metabolic function.
- Lowers LDL (bad) cholesterol
- Improves blood circulation
- Supports healthy blood sugar levels
- May improve insulin sensitivity
A review published by the National Center for Biotechnology Information
highlights ginger’s strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
How to Use Ginger
Ginger can be incorporated into daily routines in several forms:
- Fresh ginger in meals or smoothies
- Ginger tea made from sliced root
- Powdered ginger in cooking
- Capsules or extracts (supplements)
Safety and Recommended Intake
For most healthy adults, ginger is safe when consumed in moderation.
- Fresh ginger: 1–2 grams per day
- Ginger tea: 1–3 cups daily
- Powdered ginger: up to 1 teaspoon daily
Excessive intake may cause mild stomach discomfort or heartburn in sensitive individuals.
ALSO READ:
This article was prepared by the Ramsey Focus Health Desk using peer-reviewed research and evidence-based analysis.